Fiber networks are being built all over the country with the push for rural areas to have access to fast internet. Fiber optic cables use light to transmit data faster and more reliably than traditional copper wire, but it takes time to get fiber-optic infrastructure built. There are multiple steps in constructing a fiber network, which we have outlined for you below.
Step 1: Planning
Before physical construction ever begins, Socket will survey an area and identify the best way to create or expand the fiber network. At this stage Socket will figure out the amount of materials needed for the build and where to place equipment.
Step 2: Permits
Once the design is finished, the next step is acquiring all the necessary permits before physical construction can begin. Depending on your location, this can include permits from local governments, railroad companies, property owners, and utility companies. The length of time for acquiring permits can range from days to months.
Step 3: Locates
The next step involves marking underground utilities for Socket to avoid when digging the trench for fiber-optic cable. These are marked by small yard flags or spray paint. Please don’t remove these! Mini yard signs with contractor contact information will also be placed if you have any questions.
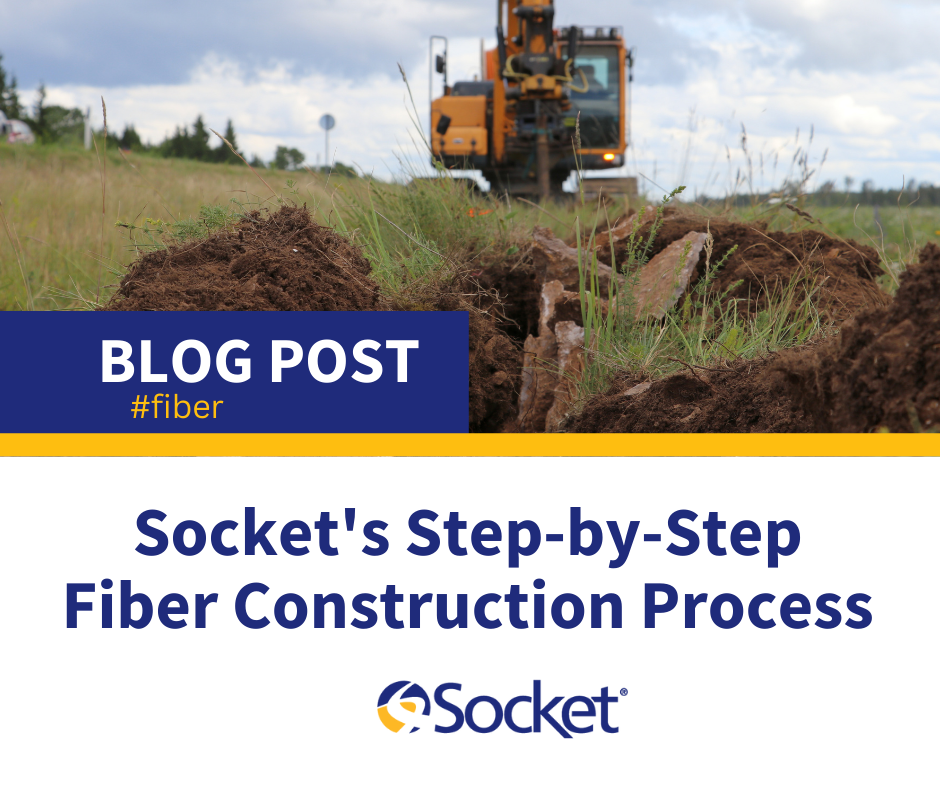
Step 4: Main Line Construction Begins
This is the stage where physical construction begins. Trenches are dug along the determined path of the fiber-optic cable within the easement or right-of-way. Fiber can also be attached aerially to existing utility poles. Sometimes the construction process involves a combination of both. Once the trench is dug, the conduit can be placed and fiber is pulled through it.
Step 5: Splitter Design and Splicing
Our engineers will move to the splitter design process. In this stage we figure out the best location for the passive optical network (PON) splitters. In order to do this, we factor in the location and density of subscribers in that area. Once splitter design is complete, splicing takes place.
Step 6: Drops
Drop lines are individual strands of fiber, which are pulled from the main line to individual homes. This is a no contact portion of the process as the customer does not need to be home while we are working outside. Once this portion is complete, Socket will reach out to schedule the on-site installation.
Step 7: In-Home Installation
At the time of installation, the technician will need to drill a hole to feed the fiber jumper inside of the home, and then fill that hole with silicone. The Socket Optical Network Terminal (ONT) will be installed inside the home opposite that wall. Whether you rent a router or supply your own, a CAT5E or CAT6 Ethernet cable will connect from the Socket ONT to the router for service connection. The installation technician will connect Socket’s equipment to confirm services at the time of installation.
That’s it! You are now connected with Socket fiber internet. If you have additional questions, feel free to give us a call at 1-800-SOCKET3. If you’re interested in bringing Socket services to your home, check to see if you’re in one of our service areas. If you are not in a current service area, we encourage you and your neighbors to express interest in Socket fiber. This is one of the factors we take into consideration when deciding where to build in the future.

